James Webb Space Telescope Discovery
Clicking on each image will open the full resolution one. Try it!Clicking on "Raw images" image will yield all the relevant raw images.
Webb Discovers Methane, Carbon Dioxide in Atmosphere of Exoplanet K2-18 b
Spectrum of K2-18 b, obtained with Webb’s NIRISS (Near-Infrared Imager and Slitless Spectrograph) and NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph), displays an abundance of methane and carbon dioxide in the exoplanet’s atmosphere, as well as a possible detection of a molecule called dimethyl sulfide (DMS). The detection of methane and carbon dioxide, and shortage of ammonia, are consistent with the presence of an ocean underneath a hydrogen-rich atmosphere in K2-18 b. K2-18 b, 8.6 times as massive as Earth, orbits the cool dwarf star K2-18 in the habitable zone and lies 120 light-years from Earth.
Credit: NASA, CSA, ESA, J. Olmstead (STScI), N. Madhusudhan (Cambridge University)
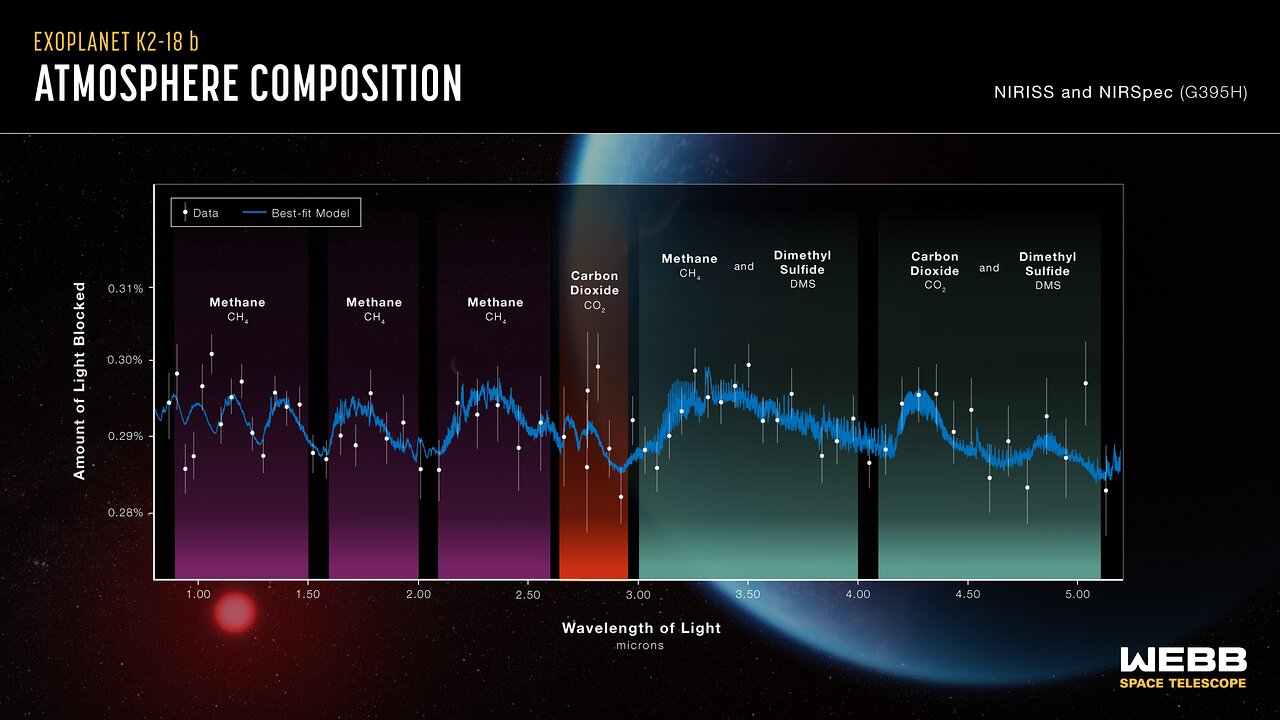 Spectra of exoplanet K2-18 b
Spectra of exoplanet K2-18 b
This artist’s concept shows what exoplanet K2-18 b could look like based on science data. K2-18 b, an exoplanet 8.6 times as massive as Earth, orbits the cool dwarf star K2-18 in the habitable zone and lies 120 light-years from Earth. A new investigation with the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope into K2-18 b has revealed the presence of carbon-bearing molecules including methane and carbon dioxide. The abundance of methane and carbon dioxide, and shortage of ammonia, support the hypothesis that there may be an ocean underneath a hydrogen-rich atmosphere in K2-18 b.
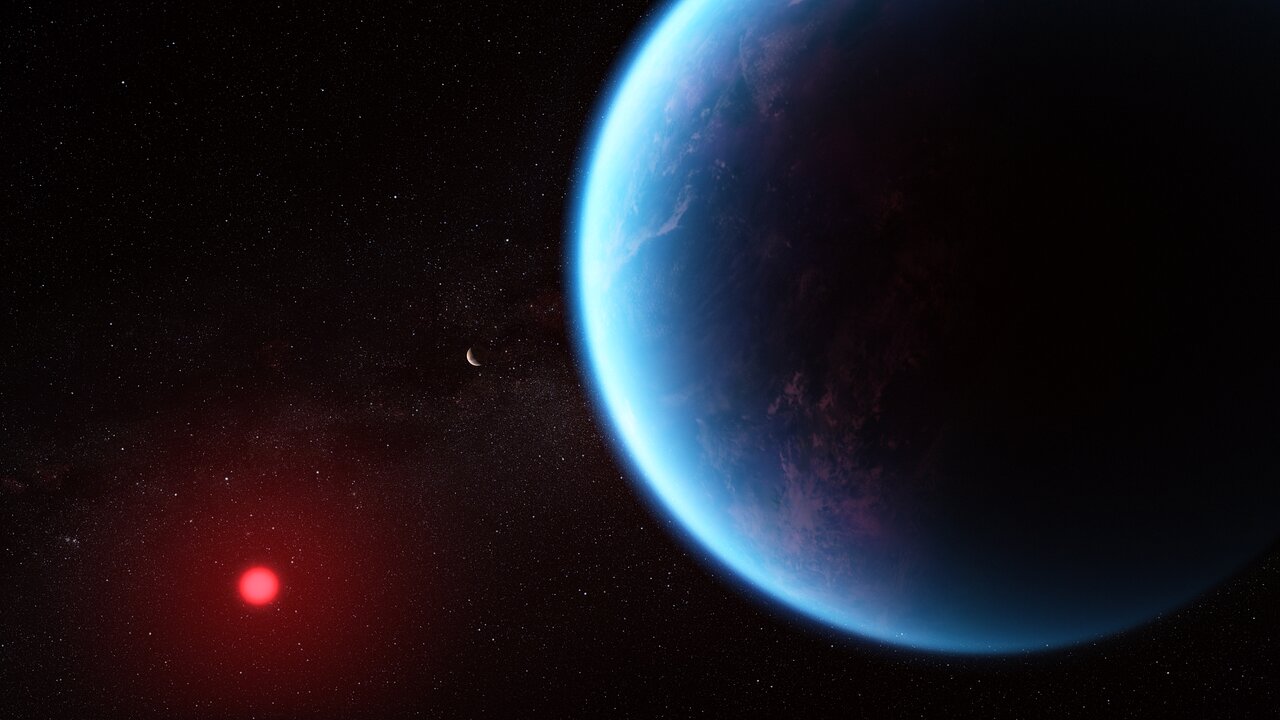 Exoplanet K2-18 b (illustration)
Exoplanet K2-18 b (illustration)