James Webb Space Telescope Discovery
Clicking on each image will open the full resolution one. Try it!Clicking on "Raw images" image will yield all the relevant raw images.
Webb Makes First Detection of Heavy Element From Star Merger
A team of scientists has used the NASA/ESA/CSA James Webb Space Telescope to observe an exceptionally bright gamma-ray burst, GRB 230307A, and its associated kilonova. Kilonovas—an explosion produced by a neutron star merging with either a black hole or with another neutron star—are extremely rare, making it difficult to observe these events. The highly sensitive infrared capabilities of Webb helped scientists identify the home address of the two neutron stars that created the kilonova.
This image from Webb’s NIRCam (Near-Infrared Camera) instrument highlights GRB 230307A’s kilonova and its former home galaxy among their local environment of other galaxies and foreground stars. The neutron stars were kicked out of their home galaxy and travelled the distance of about 120,000 light-years, approximately the diameter of the Milky Way galaxy, before finally merging several hundred million years later.
This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the James Webb Space Telescope using the NIRCam instrument. Several filters were used to sample wide wavelength ranges. The colour results from assigning different hues (colours) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colours are: Blue: F115W + F150W Green: F277W Red: F356W + F444W
Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, STScI, A. Levan (IMAPP, Warw), A. Pagan (STScI)
 Kilonova and host galaxy
Kilonova and host galaxy
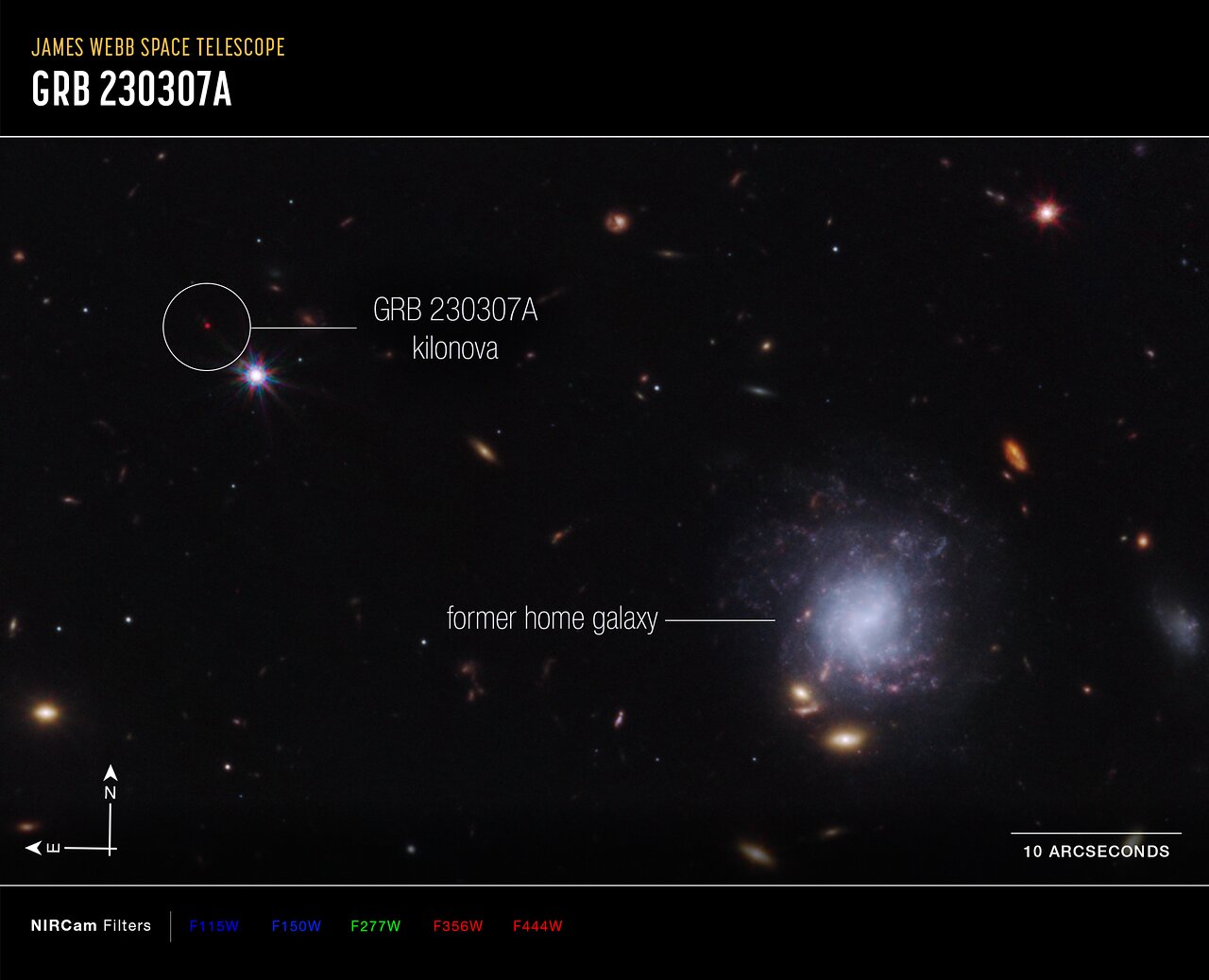 Kilonova and host galaxy (annotated)
Kilonova and host galaxy (annotated)
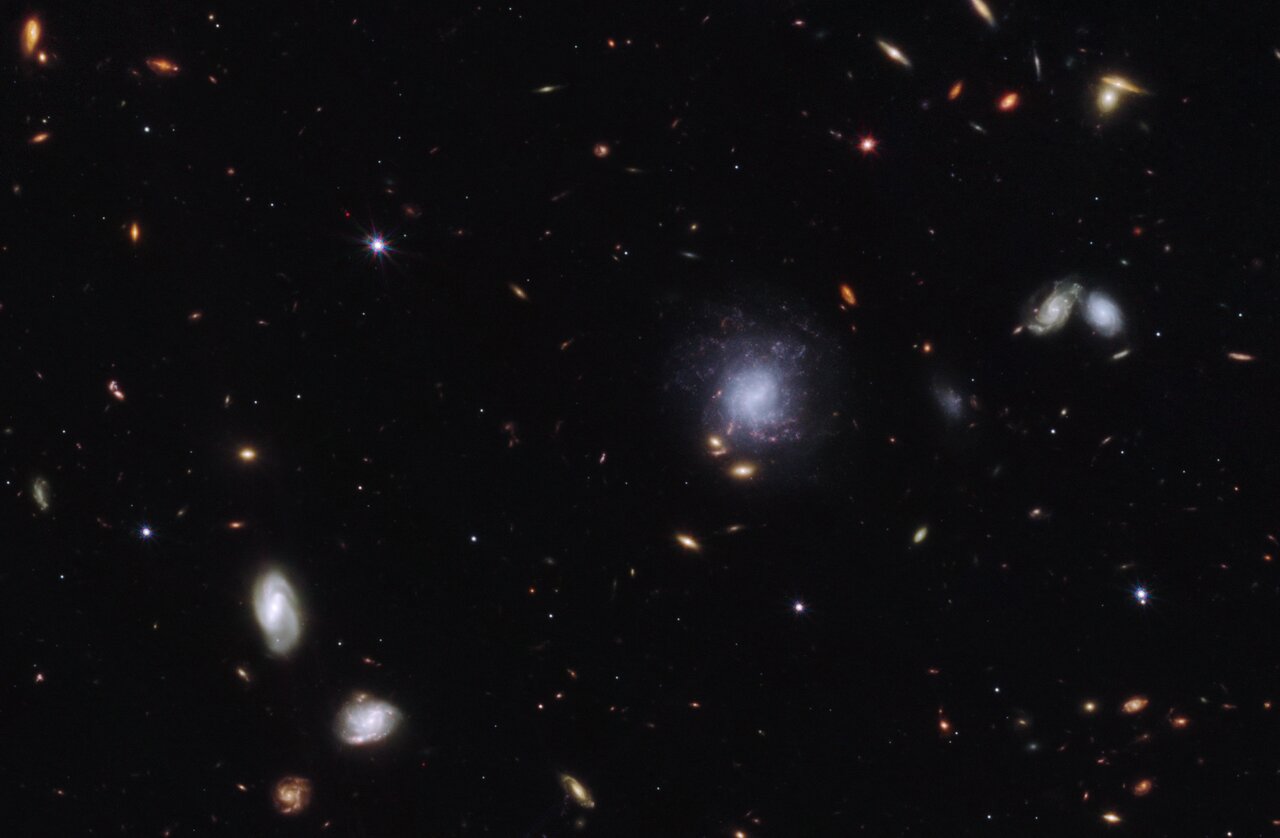 Kilonova and host galaxy (clean)
Kilonova and host galaxy (clean)
This graphic presentation compares the spectral data of GRB 230307A’s kilonova as observed by the James Webb Space Telescope and a kilonova model. Both show a distinct peak in the region of the spectrum associated with tellurium, with the area shaded in red. The detection of tellurium, which is rarer than platinum on Earth, marks Webb’s first direct look at an individual heavy element from a kilonova.
Though astronomers have theorised neutron star mergers to be the ideal environment to create chemical elements, including some that are essential to life, these explosive events—known as kilonovas—are rare and rapid. Webb’s NIRSpec (Near-Infrared Spectrograph) acquired a spectrum of GRB 230307A’s kilonova, helping scientists secure evidence of the synthesis of heavy elements from neutron star mergers.
With Webb’s extraordinary ability to look further into space than ever before, astronomers expect to find even more kilonovas and acquire further evidence of heavy element creation.
Credit: NASA, ESA, CSA, J. Olmsted (STScI)
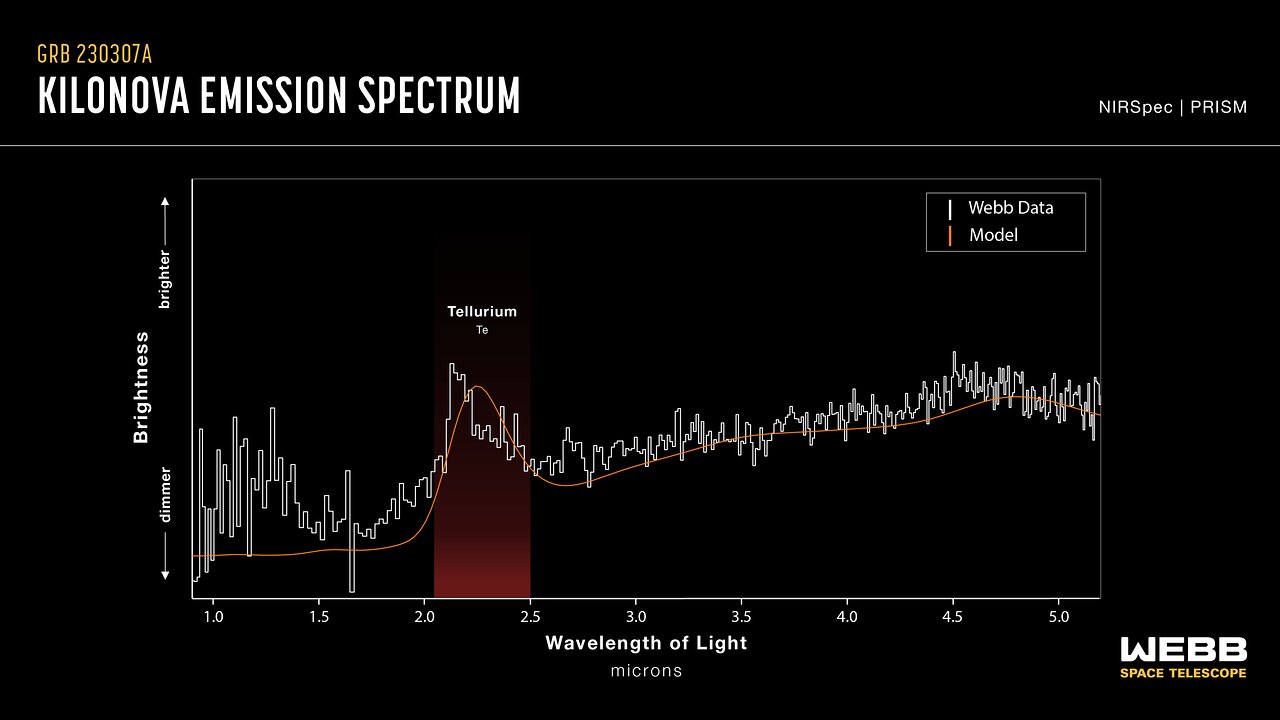 Kilonova emission spectrum
Kilonova emission spectrum
 Article images (unofficial)
Article images (unofficial)
 Raw images
Raw images